Norton’s Theorem
This theorem is another to the Thevenin’s theorem. In fact, it's the twin of Thevenin’s theorem. Whereas Thevenin’s theorem reduces a two-terminal active network of linear resistances and generators to a similar constant-voltage supply and series resistance, Norton’s theorem replaces the network by a similar constant-current supply and a parallel resistance.
This theorem could also be declared as follows :
(i) Any two-terminal active network containing voltage sources and resistance once viewed from its output terminals , is adore a constant-current supply and a parallel resistance. The constant current is capable this which might flow in a very short-circuit placed across the terminals and parallel resistance is that the resistance of the network once viewed from these opencircuited terminals finally voltage and current sources are removed and replaced by their internal resistances.
Explanation
As seen from Fig. 2.202 (a), a brief is placed across the terminals A and B of the network with all its energy sources gift. The short-circuit current ISC provides the worth of constant-current supply. for locating Little Rhody, all sources are removed as shown in Fig. 2.202 (b). The resistance of the network once looked into from terminals A and B provides Little Rhody.
The Norton’s* equivalent circuit is shown in Fig. 2.202 (c). It consists of a perfect constantcurrent supply of infinite internal resistance (Art. 2.16) having a resistance of Little Rhody connected in parallel with it. solved Examples a pair of.96, 2.97 and 2.98 etc. illustrate this procedure
. (ii) Another helpful generalized kind of this theorem is as follows :
The voltage between any 2 points during a network is up to ISC. Little Rhody wherever ISC is that the shortcircuit current between the 2 points and Little Rhody is that the resistance of the network as viewed from these points with all voltage sources being replaced by their internal resistances (if any) and current sources replaced by open-circuits.
Suppose, it's needed to seek out the voltage across resistance R3 and thence current through it [Fig. 2.202 (d)]. If short-circuit is placed between A and B, then current in it because of battery of e.m.f. E1 is E1/R1 and because of the opposite battery is E2/R2.
where G1 and G2 square measure branch conductances.
Now, the interior resistance of the network as viewed from A and B merely consists of 3 resistances R1, R2 and R3 connected in parallel between A and B. Please note that here load resistance R3 has not been removed. within the 1st methodology given on top of, it's to be removed.
How To Nortonize a Given Circuit ?
This procedure is predicated on the primary statement of the theory given higher than.
1. take away the resistance (if any) across the 2 given terminals and place a short-circuit across them.
2. cipher the short-circuit current ISC.
3. take away all voltage sources however retain their internal resistances, if any. Similarly, take away all current sources and replace them by open-circuits i.e. by infinite resistance.
4. Next, realize the resistance R1 (also known as RN) of the network as looked into from the given terminals. it's precisely the same as Rth (Art. 2.16).
5. this supply (ISC) joined in parallel across Rhode Island between the 2 terminals offers Norton’s equivalent circuit.
Thanks by Rana Arslan..
This theorem is another to the Thevenin’s theorem. In fact, it's the twin of Thevenin’s theorem. Whereas Thevenin’s theorem reduces a two-terminal active network of linear resistances and generators to a similar constant-voltage supply and series resistance, Norton’s theorem replaces the network by a similar constant-current supply and a parallel resistance.
This theorem could also be declared as follows :
(i) Any two-terminal active network containing voltage sources and resistance once viewed from its output terminals , is adore a constant-current supply and a parallel resistance. The constant current is capable this which might flow in a very short-circuit placed across the terminals and parallel resistance is that the resistance of the network once viewed from these opencircuited terminals finally voltage and current sources are removed and replaced by their internal resistances.
Explanation
As seen from Fig. 2.202 (a), a brief is placed across the terminals A and B of the network with all its energy sources gift. The short-circuit current ISC provides the worth of constant-current supply. for locating Little Rhody, all sources are removed as shown in Fig. 2.202 (b). The resistance of the network once looked into from terminals A and B provides Little Rhody.
The Norton’s* equivalent circuit is shown in Fig. 2.202 (c). It consists of a perfect constantcurrent supply of infinite internal resistance (Art. 2.16) having a resistance of Little Rhody connected in parallel with it. solved Examples a pair of.96, 2.97 and 2.98 etc. illustrate this procedure
. (ii) Another helpful generalized kind of this theorem is as follows :
The voltage between any 2 points during a network is up to ISC. Little Rhody wherever ISC is that the shortcircuit current between the 2 points and Little Rhody is that the resistance of the network as viewed from these points with all voltage sources being replaced by their internal resistances (if any) and current sources replaced by open-circuits.
Suppose, it's needed to seek out the voltage across resistance R3 and thence current through it [Fig. 2.202 (d)]. If short-circuit is placed between A and B, then current in it because of battery of e.m.f. E1 is E1/R1 and because of the opposite battery is E2/R2.
where G1 and G2 square measure branch conductances.
Now, the interior resistance of the network as viewed from A and B merely consists of 3 resistances R1, R2 and R3 connected in parallel between A and B. Please note that here load resistance R3 has not been removed. within the 1st methodology given on top of, it's to be removed.
How To Nortonize a Given Circuit ?
1. take away the resistance (if any) across the 2 given terminals and place a short-circuit across them.
2. cipher the short-circuit current ISC.
3. take away all voltage sources however retain their internal resistances, if any. Similarly, take away all current sources and replace them by open-circuits i.e. by infinite resistance.
4. Next, realize the resistance R1 (also known as RN) of the network as looked into from the given terminals. it's precisely the same as Rth (Art. 2.16).
5. this supply (ISC) joined in parallel across Rhode Island between the 2 terminals offers Norton’s equivalent circuit.
Thanks by Rana Arslan..
Norton’s Theorem And How To Nortonize a Given Circuit ?
 Reviewed by I will write articles or blogs containing 500 words for you.....
on
April 10, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by I will write articles or blogs containing 500 words for you.....
on
April 10, 2019
Rating:
 Reviewed by I will write articles or blogs containing 500 words for you.....
on
April 10, 2019
Rating:
Reviewed by I will write articles or blogs containing 500 words for you.....
on
April 10, 2019
Rating:


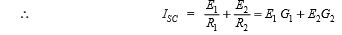






No comments: